在Ubuntu 14.04上部署OpenStack Juno
1 规划
192.168.234.202 Openstack controller node
192.168.234.205 Openstack network node
192.168.234.204 Openstack compute node
networ node必须有三个NIC(network interface card),也就是网卡.
管理网段:10.0.0.0/24
2 基础环境
2.1 控制节点 controller node
要给它分配一个OpenStack管理网段的IP,因为它已经有了一个192段的IP了,所以建一个虚拟网卡绑定OpenStack管理网段的IP。
/etc/network/interfaces
{% highlight aconf %}
This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
The loopback network interface
auto lo iface lo inet loopback
The primary network interface
auto eth0 #iface eth0 inet dhcp iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.234.202 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.234.1
OpenStack management interface.
iface eth0:1 inet static address 10.0.0.11 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 10.0.0.1
{% endhighlight %}
/etc/hosts
{% highlight sh %}
Controller
10.0.0.11 controller
network
10.0.0.21 network
compute1
10.0.0.31 compute1 {% endhighlight %}
2.2 网络节点 network node
/etc/network/interfaces
{% highlight aconf %} #The primary network interface auto eth0 iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.234.205 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.234.1
#management interface auto eth1:1 iface eth0:1 inet static address 10.0.0.21 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 10.0.0.1
#Instance tunnels interface. auto eth1:2 iface eth0:2 inet static address 10.0.1.21 netmask 255.255.255.0 {% endhighlight %}
/etc/hosts
{% highlight sh %} #Controller 10.0.0.11 controller
#network 10.0.0.21 network
#compute1 10.0.0.31 compute1 {% endhighlight %}
2.3 计算节点 compute node
/etc/network/interfaces
{% highlight sh %}
The primary network interface
auto eth0 #iface eth0 inet dhcp iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.234.204 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.234.1
#management interface auto eth0:1 iface eth0:1 inet static address 10.0.0.31 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 10.0.0.1
#Instance tunnels interface. auto eth0:2 iface eth0:2 inet static address 10.0.1.31 netmask 255.255.255.0
{% endhighlight %}
/etc/hosts
{% highlight sh %} #Controller 10.0.0.11 controller
#network 10.0.0.21 network
#compute1 10.0.0.31 compute1 {% endhighlight %}
3 配置时间同步
所有节点的时间必须同步
3.1 控制节点ntp配置
安装ntp {% highlight sh %} $ sudo aptitude install ntp -y {% endhighlight %}
在/etc/ntp.conf配置上中国区的server. {% highlight sh %} server 1.cn.pool.ntp.org server 0.asia.pool.ntp.org server 3.asia.pool.ntp.org {% endhighlight %}
{% highlight sh %} server NTP_SERVER iburst restrict -4 default kod notrap nomodify restrict -6 default kod notrap nomodify {% endhighlight %}
注意:默认的配置里的restrict有两个选项nopeer 和 noquery必须去掉。
重启服务 {% highlight sh %}
service ntp restart
{% endhighlight %}
3.2 其它节点ntp配置
网络节点和计算节点也要安装配置ntp,要注意的是它们的ntp配置文件指定的server是controller,也就是从控制节点同步时间。
{% highlight sh %} server controller iburst {% endhighlight %}
3.3 验证ntp是否正确安装
1 在控制节点上运行此命令
{% highlight sh %} #ntpq -c peers remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
dns2.synet.edu. 202.118.1.46 2 u 67 64 11 114.585 6.251 52.688 *ts0.itsc.cuhk.e .GPS. 1 u 64 64 37 79.028 -37.503 17.905 web10.hnshostin 193.67.79.202 2 u 4 64 77 474.192 -58.614 12.22 {% endhighlight %} 你的输出可能跟我的不一样,没关系有内容就OK。
2 在控制节点上运行此命令 {% highlight sh %}
ntpq -c assoc
ind assid status conf reach auth condition last_event cnt
1 61846 9424 yes yes none candidate reachable 2 2 61847 963a yes yes none sys.peer sys_peer 3 3 61848 9324 yes yes none outlyer reachable 2 4 61849 9424 yes yes none candidate reachable 2 {% endhighlight %} 你的输出可能跟我的不一样,没关系有内容就OK。
3 在其它节点上运行此命令
{% highlight sh %} ntpq -c peers remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
*controller 137.189.4.10 2 u 29 64 1 0.154 18.278 0.610 {% endhighlight %}
输出结果中的remote列,应该是控制节点的hostname.
4 在其它节点上运行下面的命令 {% highlight sh %}
ntpq -c assoc
ind assid status conf reach auth condition last_event cnt
1 45051 963a yes yes none sys.peer sys_peer 3 {% endhighlight %}
condition列的值应该是sys.peer
4 安装MySQL RabbitMQ
4.1 安装Ubuntu Cloud的keyring和仓库
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install ubuntu-cloud-keyring
echo “deb http://ubuntu-cloud.archive.canonical.com/ubuntu" \
“trusty-updates/juno main” > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cloudarchive-juno.list {% endhighlight %}
4.2 安装配置数据库
1 安装MySQL
在数据库只需要安装在controller节点上。
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install mysql-server python-mysqldb
{% endhighlight %} 在安装时要求输入root用户的密码,在本文里统一用openstack这个密码了。
2 编辑/etc/mysql/my.cnf,完成下面所提的操作。
- 在[mysqld]这一节里,把mysql绑定的IP改为controller节点的管理网段IP,同时加上下面的选项。
{% highlight sh %} [mysqld] … bind-address = 10.0.0.11 … default-storage-engine = innodb innodb_file_per_table collation-server = utf8_general_ci init-connect = ‘SET NAMES utf8’ character-set-server = utf8 {% endhighlight %}
重启mysql服务。
4.3 安装消息服务
OpenStack使用消息中间件来传递服务之间的操作和状态,消息中间件通常安装在控制节点。OpenStack支持几种消息中间件,这里我们安装最常用的RabbitMQ。
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install rabbitmq-server
{% endhighlight %}
配置RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ在安装时创建了一个用户guest,我们就用这个用户了,只是把他的密码修改为openstack
# rabbitmqctl change_password guest openstack
For RabbitMQ version 3.3.0 or newer, you must enable remote access for the guest account.
Check the RabbitMQ version:
# rabbitmqctl status | grep rabbit
Restart the message broker service:
# service rabbitmq-server restart
5 安装OpenStack的认证服务 OpenStack Identity service
OpenStack Identity service提供如下功能
- 记录用户和他们的权限
- 提供OpenStack可用服务的API列表 所有的服务在安装后都要向Identity service注册自己。Identity service知道当前安装了哪些服务和他们在网络中的位置。
5.1 安装配置Identity service
5.1.1 准备工作
1 首先创建数据库
登录到控制节点的mysql {% highlight sh %} $ mysql -u root -p {% endhighlight %}
创建数据库 {% highlight sql %} CREATE DATABASE keystone; {% endhighlight %}
加上本地和远程访问这个keystone数据库的权限。
{% highlight sql %}
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON keystone.* TO ‘keystone’@’localhost’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON keystone.* TO ‘keystone’@’%’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’;
flush PRIVILEGES;
{% endhighlight %}
生成管理员的token,在初始配置时用。
{% highlight sh %}
openssl rand -hex 10
7212bf54588f88818b52 {% endhighlight %}
5.1.1 安装配置keystone
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install keystone python-keystoneclient
{% endhighlight %}
编辑 /etc/keystone/keystone.conf完成下面的操作:
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] admin_token = 7212bf54588f88818b52 verbose = True … [database] connection = mysql://keystone:openstack@controller/keystone … [token] #这个provider可以不用改,默认的就是uuid provider = keystone.token.providers.uuid.Provider
#这个默认是注释掉的,我们去掉注释就好 driver = keystone.token.persistence.backends.sql.Token … [revoke] driver = keystone.contrib.revoke.backends.sql.Revoke … {% endhighlight %}
然后重启一下keystone服务就行了。 {% highlight sh %}
service keystone restart
{% endhighlight %}
5.2 创建tenants, users, and roles
5.2.1 准备工作
在安装完Identity service后,你要创建tenants租户(也就是projects)、用户和角色。
你要用我们上一节创建的临时的管理员token,在你运行keystone命令前,手动配置Identity service endpoint。
你可以把管理员token用–os-token这个参数传给keystone命令,也可以设置环境变量OS_SERVICE_TOKEN。一样的,你可以把管理员token用 Identity service的endpoint用命令行参数–os-endpoint传给keystone,也可以设置环境变量–os-endpoint。
我们采用环境变量的方式
{% highlight sh %} $ export OS_SERVICE_TOKEN=7212bf54588f88818b52
$ export OS_SERVICE_ENDPOINT=http://controller:35357/v2.0 {% endhighlight %}
5.2.2 开始创建
- 创建一个用于管理的tenant,用户和角色
创建管理员租户 {% highlight sh %}
keystone tenant-create –name admin –description “Admin Tenant”
+————-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +————-+———————————-+ | description | Admin Tenant | | enabled | True | | id | 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 | | name | admin | +————-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
创建管理员,我们用openstack做密码。
{% highlight sh %}
keystone user-create –name admin –pass openstack –email admin@example.com
+———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | email | admin@example.com | | enabled | True | | id | c2ba205513e448098f0e0daf80f2f649 | | name | admin | | username | admin | +———-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
创建管理员角色
{% highlight sh %} $ keystone role-create –name admin +———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | id | bff3a6083b714fa29c9344bf8930d199 | | name | admin | +———-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
把管理员角色加到管理员用户上 {% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-role-add –user admin –tenant admin –role admin {% endhighlight %}
- Note:Any roles that you create must map to roles specified in the policy.json file included with each OpenStack service. The default policy for most services grants administrative access to the admin role. For more information, see the Operations Guide - Managing Projects and Users.
- 创建一个用于一般操作的普通租户和用户
{% highlight sh %} $ keystone tenant-create –name demo –description “Demo Tenant” +————-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +————-+———————————-+ | description | Demo Tenant | | enabled | True | | id | 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 | | name | demo | +————-+———————————-+
$ keystone user-create –name demo –tenant demo –pass openstack –email demo@example.com +———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | email | demo@example.com | | enabled | True | | id | 54a55d3f3c1f4797bb82d196e6c02ccd | | name | demo | | tenantId | 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 | | username | demo | +———-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
- OpenStack 服务需要租户、用户和角色来和其它的服务进行交互。每个服务都需要一个或多个
service tenant下的特定的管理员,我们先来创建这个service tenant,下节将把这些服务注册到Identity service里。
{% highlight sh %} $ keystone tenant-create –name service –description “Service Tenant” +————-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +————-+———————————-+ | description | Service Tenant | | enabled | True | | id | ef36de18149b4c809c4b26b63b6dda37 | | name | service | +————-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
5.3 创建服务和API端点
你仍然需要设置OS_SERVICE_TOKEN和OS_SERVICE_ENDPOINT 这个两个环境变量。
5.3.1 创建Identity service服务实体
Openstack维护着一个当前部署环境下可用服务的列表,一个服务想要调用另外一个服务时会先查询一下Identity service,看看想调用的服务是否可用,部署在哪儿等。
首先当然是为Identity service创建一个服务实体了。
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone service-create –name keystone –type identity
–description “OpenStack Identity”
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | OpenStack Identity |
| enabled | True |
| id | 4d17778357b84921aa632a5f02a4903b |
| name | keystone |
| type | identity |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
5.3.2 创建Identity service的API端点
OpenStack的服务都提供API以方便其它与之沟通,Identity service维护着这些服务的列表。一个服务用查询这个列表以确定如何与其它服务进行沟通。
OpenStack提供三种API端点的变体:admin, internal, and public。在生产环境里,出于安全的考虑,它们应该会部署在单独的网络里,向不同的用户提供服务。
OpenStack支持多个regions,在本文里进行了简化,我们把所有的API端点都部署在管理网里,并都归属在regionOne这个region下。
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone endpoint-create
–service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ identity / {print $2}’)
–publicurl http://controller:5000/v2.0
–internalurl http://controller:5000/v2.0
–adminurl http://controller:35357/v2.0
–region regionOne
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| adminurl | http://controller:35357/v2.0 |
| id | f6a1c6efb040455c8e5aa0b05d01266d |
| internalurl | http://controller:5000/v2.0 |
| publicurl | http://controller:5000/v2.0 |
| region | regionOne |
| service_id | 4d17778357b84921aa632a5f02a4903b |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
上面的命令keystone service-list | awk '/ identity / {print $2}'返回的其实就是我创建的Identity service实体的id.
- Note Each service that you add to your OpenStack environment requires adding information such as API endpoints to the Identity service. The sections of this guide that cover service installation include steps to add the appropriate information to the Identity service
5.4 验证安装
本节我们来验证Identity service是否正确安装。
5.4.1 删除环境变量
删除OS_SERVICE_TOKEN and OS_SERVICE_ENDPOINT 这两个环境变量。
{% highlight sh %} $ unset OS_SERVICE_TOKEN OS_SERVICE_ENDPOINT {% endhighlight %}
5.4.2 以管理员的身份来请求鉴权的标识
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone –os-tenant-name admin –os-username admin –os-password openstack
–os-auth-url http://controller:35357/v2.0 token-get
+———–+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———–+———————————-+ | expires | 2015-03-12T05:12:19Z | | id | c9fbcb91847749f89848d968f411f571 | | tenant_id | 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 | | user_id | c2ba205513e448098f0e0daf80f2f649 | +———–+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
5.4.3 查询所有的租户
以管理员的身份查询所有的租户,看看我们在前面创建的tenant是否创建成功了。
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone –os-tenant-name admin –os-username admin –os-password openstack
–os-auth-url http://controller:35357/v2.0 tenant-list
+———————————-+———+———+
| id | name | enabled |
+———————————-+———+———+
| 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 | admin | True |
| 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 | demo | True |
| ef36de18149b4c809c4b26b63b6dda37 | service | True |
+———————————-+———+———+
{% endhighlight %}
5.4.4 查询所有的用户
以管理员的身份查询所有的租户,看看我们在前面创建的用户是否都在。
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone –os-tenant-name admin –os-username admin –os-password openstack
–os-auth-url http://controller:35357/v2.0 user-list
+———————————-+——-+———+——————-+
| id | name | enabled | email |
+———————————-+——-+———+——————-+
| c2ba205513e448098f0e0daf80f2f649 | admin | True | admin@example.com |
| 54a55d3f3c1f4797bb82d196e6c02ccd | demo | True | demo@example.com |
+———————————-+——-+———+——————-+
{% endhighlight %}
admin和demo这个用户必须都在才对。
5.4.5 查询所有的角色
以管理员的身份查询所有的租户,看看我们在前面创建的角色是否都在。
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone –os-tenant-name admin –os-username admin –os-password openstack
–os-auth-url http://controller:35357/v2.0 role-list
+———————————-+———-+
| id | name |
+———————————-+———-+
| 9fe2ff9ee4384b1894a90878d3e92bab | member |
| 92b557ad2c944613a15065d267480802 | admin |
+———————————-+———-+
{% endhighlight %}
5.4.6 获得demo用户鉴权的标识
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone –os-tenant-name demo –os-username demo –os-password openstack
–os-auth-url http://controller:35357/v2.0 token-get
+———–+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+———–+———————————-+
| expires | 2015-03-12T05:57:19Z |
| id | 03732cde3a5941bfa7db76515b5422a2 |
| tenant_id | 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 |
| user_id | 54a55d3f3c1f4797bb82d196e6c02ccd |
+———–+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
5.4.7 demo用户尝试查询所有用户
demo用户没有管理权限,所以应该报403错误。
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone –os-tenant-name demo –os-username demo –os-password openstack
–os-auth-url http://controller:35357/v2.0 user-list
You are not authorized to perform the requested action: admin_required (HTTP 403)
{% endhighlight %}
5.5 创建OpenStack客户端环境脚本
上一节我们用环境变量加命令行参数的方式用keystone这个命令来与Identity service来交互。为了提高客户端的操作效率,OpenStack支持简单客户端环境脚本- OpenRC文件。这些脚本包含所有客户端共用的一些选项,当然也可以包含特定选项。
更多信息请参考OpenStack用户指南。
编辑admin-openrc.sh,键入以下内容: {% highlight sh %} export OS_TENANT_NAME=admin export OS_USERNAME=admin export OS_PASSWORD=openstack export OS_AUTH_URL=http://controller:35357/v2.0 {% endhighlight %}
编辑demo-openrc.sh,键入以下内容: {% highlight sh %} export OS_TENANT_NAME=demo export OS_USERNAME=demo export OS_PASSWORD=openstack export OS_AUTH_URL=http://controller:5000/v2.0 {% endhighlight %}
加载这些脚本,比如你想以管理员的身份来操作,请运行: {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
6 安装image服务
OpenStack Image Service(glance)允许用户发现、注册和检索虚拟机的映像。它提供了一个REST API,你可以用它来查询映像的元信息和检索映像。 你可以把映像放在安装image service本地文件系统里,也可以选择放在对象存储系统里,如 OpenStack Object Storage。
重要 本文将把Image Service(glance)安装在控制节点上,并使用本地文件保存映像,默认目录为/var/lib/glance/images/,请确保控制节点有足够的存储空间。 如果想了解Image Service(glance)所使用的后端存储的信息更多信息,请参考Configuration Reference。
6.1 OpenStack映像服务
OpenStack映像服务是它的IasS的重要核心组件,它接受磁盘或服务器映像的API请求,向用户或OpenStack的计算组件提供映像的元数据。
一些运行在OpenStack Image Service上的周期性的进程支持缓存功能。复制服务通过集群来确保一致性和可用性。其它的服务还包含审核服务,更新服务和收割服务。
OpenStack Image Service包含以下组件:
glance-api 接受映像发现、检索和存储的API调用。
glance-registry Stores, processes, and retrieves metadata about images. Metadata includes items such as size and type. 存储、处理和检索映像的元数据,元数据包含它的大小和类型。
Note 安全备注
glance-registry是内部私有服务,只向OpenStack映像服务提供服务,不要把它暴露给用户。
数据库 用来保存映像的元数据。
映像存储仓库 支持各种存储仓库,包括一般文件系统,对象存储系统,RADOS块设备,HTTP和Amazon S3。
6.2 安装和配置OpenStack映像服务
6.2.1 安装准备
在安装前,你必须创建数据库,服务凭证和API端点。
- 配置数据库 数据库安装在控制节点上。
{% highlight sh %} $ mysql -u root -p {% endhighlight %}
创建 glance 数据库 {% highlight sql %} CREATE DATABASE glance;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON glance.* TO ‘glance’@’localhost’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON glance.* TO ‘glance’@’%’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’;
{% endhighlight %}
用切换到管理员身份 {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
创建服务凭证
创建glance用户
{% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-create –name glance –pass openstack +———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | email | | | enabled | True | | id | 924b65933a294f0bb5e26945689c2c38 | | name | glance | | username | glance | +———-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
为glance用户添加admin角色: {% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-role-add –user glance –tenant service –role admin {% endhighlight %}
创建 glance 服务实体:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone service-create –name glance –type image
–description “OpenStack Image Service”
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | OpenStack Image Service |
| enabled | True |
| id | 1c95672e6b354cddaf6ce0115b6042ab |
| name | glance |
| type | image |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
创建Image Service API 端点:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone endpoint-create
–service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ image / {print $2}’)
–publicurl http://controller:9292
–internalurl http://controller:9292
–adminurl http://controller:9292
–region regionOne
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| adminurl | http://controller:9292 |
| id | ef72bb245bca419399cf4ff304148c31 |
| internalurl | http://controller:9292 |
| publicurl | http://controller:9292 |
| region | regionOne |
| service_id | 1c95672e6b354cddaf6ce0115b6042ab |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
6.2.2 创建配置Image服务组件
1 安装包
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install glance python-glanceclient
{% endhighlight %}
2 编辑/etc/glance/glance-api.conf 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %} [database] connection = mysql://glance:GLANCE_DBPASS@controller/glance … [keystone_authtoken]
#Note:Comment out any auth_host, auth_port, and auth_protocol options because the identity_uri option replaces them. auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = glance admin_password = GLANCE_PASS … [paste_deploy] flavor = keystone …
[glance_store] … default_store = file filesystem_store_datadir = /var/lib/glance/images/
[DEFAULT] … notification_driver = noop [DEFAULT] … verbose = True {% endhighlight %}
在本文中GLANCE_DBPASS和GLANCE_PASS都为openstack.
3 编辑 /etc/glance/glance-registry.conf 加入下面的内容:
{% highlight ini %} [database] … connection = mysql://glance:GLANCE_DBPASS@controller/glance
[keystone_authtoken] … auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = glance admin_password = GLANCE_PASS
[paste_deploy] … flavor = keystone
[DEFAULT] … notification_driver = noop verbose = True
{% endhighlight %}
Note: 请注释掉任何auth_host、auth_port和auth_protocol 选项 因为identity_uri替换了它们.
4 装载Image Service数据库: {% highlight sh %}
su -s /bin/sh -c “glance-manage db_sync” glance
{% endhighlight %}
6.2.3 完成安装
重启Image服务:
{% highlight sh %}
service glance-registry restart
service glance-api restart
{% endhighlight %}
默认Ubuntu安装创建了一个SQLite,你可以删除它。 {% highlight sh %}
rm -f /var/lib/glance/glance.sqlite
{% endhighlight %}
6.3 验证安装
[1] 创建一个临时目录 {% highlight sh %} $ mkdir /tmp/images {% endhighlight %}
2 下载映像到这个临时目录 {% highlight sh %} $ wget -P /tmp/images http://cdn.download.cirros-cloud.net/0.3.3/cirros-0.3.3-x86_64-disk.img {% endhighlight %}
3 转成管理员身份 {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
4 上传映像到Image服务
{% highlight sh %}
$ glance image-create –name “cirros-0.3.3-x86_64” –file /tmp/images/cirros-0.3.3-x86_64-disk.img
–disk-format qcow2 –container-format bare –is-public True –progress
[=============================>] 100% +——————+————————————–+ | Property | Value | +——————+————————————–+ | checksum | 133eae9fb1c98f45894a4e60d8736619 | | container_format | bare | | created_at | 2015-03-12T08:45:49 | | deleted | False | | deleted_at | None | | disk_format | qcow2 | | id | b460412b-4566-4d8b-8b9a-27f638f8ca58 | | is_public | True | | min_disk | 0 | | min_ram | 0 | | name | cirros-0.3.3-x86_64 | | owner | 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 | | protected | False | | size | 13200896 | | status | active | | updated_at | 2015-03-12T08:45:49 | | virtual_size | None | +——————+————————————–+ {% endhighlight %}
glance image-create命令的更多信息请参见:OpenStack Command-Line Interface Reference.
关于disk和container格式的更多信息请参考OpenStack Virtual Machine Image Guide
5 查询映像以确认数据是否正确
{% highlight sh %}
$ glance image-list
+————————————–+———————+————-+——————+———-+——–+
| ID | Name | Disk Format | Container Format | Size | Status |
+————————————–+———————+————-+——————+———-+——–+
| b460412b-4566-4d8b-8b9a-27f638f8ca58 | cirros-0.3.3-x86_64 | qcow2 | bare | 13200896 | active |
+————————————–+———————+————-+——————+———-+——–+
{% endhighlight %}
6 删除临时目录
{% highlight sh %}
$ rm -r /tmp/images
{% endhighlight %}
7 安装OpenStack计算服务
概念和组件的作用,请参考安装手册
7.1 安装配置控制节点
7.1.1 准备工作
1 配置数据库 数据库安装在控制节点上。
{% highlight sh %} $ mysql -u root -p {% endhighlight %}
创建 glance 数据库 {% highlight sql %} CREATE DATABASE nova;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON nova.* TO ’nova’@’localhost’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘NOVA_DBPASS’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON nova.* TO ’nova’@’%’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘NOVA_DBPASS’;
{% endhighlight %}
NOVA_DBPASS我们使用openstack.
2 切换到管理员身份 {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
3 To create the service credentials, complete these steps:
创建 nova 用户: {% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-create –name nova –pass openstack +———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | email | | | enabled | True | | id | 952eae64d8124b06812a5bb595f3690f | | name | nova | | username | nova | +———-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
为nova用户添加admin角色: {% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-role-add –user nova –tenant service –role admin {% endhighlight %}
创建 nova 服务实体:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone service-create –name nova –type compute
–description “OpenStack Compute”
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | OpenStack Compute |
| enabled | True |
| id | 45a5a2e53de246f89dedf20a9d23c8f8 |
| name | nova |
| type | compute |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
创建计算服务API端点:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone endpoint-create
–service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ compute / {print $2}’)
–publicurl http://controller:8774/v2/%(tenant_id)s
–internalurl http://controller:8774/v2/%(tenant_id)s
–adminurl http://controller:8774/v2/%(tenant_id)s
–region regionOne
+————-+—————————————–+
| Property | Value |
+————-+—————————————–+
| adminurl | http://controller:8774/v2/%(tenant_id)s |
| id | 7839d34cdfb641a9884eee7b67680391 |
| internalurl | http://controller:8774/v2/%(tenant_id)s |
| publicurl | http://controller:8774/v2/%(tenant_id)s |
| region | regionOne |
| service_id | 45a5a2e53de246f89dedf20a9d23c8f8 |
+————-+—————————————–+
{% endhighlight %}
7.1.2 安装配置计算控制组件
1 安装相关包 {% highlight sh %}
apt-get install nova-api nova-cert nova-conductor nova-consoleauth \
nova-novncproxy nova-scheduler python-novaclient {% endhighlight %}
2 编辑 /etc/nova/nova.conf 加入下面的内容
默认安装nova.conf内容好少,你要手动添加下面的内容。
{% highlight ini %}
[database]
…
connection = mysql://nova:openstack@controller/nova
[DEFAULT] … rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack auth_strategy = keystone #这个IP应该是管理网段的IP my_ip = 10.0.0.11 vncserver_listen = 10.0.0.11 vncserver_proxyclient_address = 10.0.0.11 verbose = True [keystone_authtoken] … auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = nova admin_password = openstack
[glance] … host = controller {% endhighlight %}
3 装载计算服务数据库: {% highlight sh %}
su -s /bin/sh -c “nova-manage db sync” nova
{% endhighlight %}
7.1.3 完成安装
重启计算服务 {% highlight sh %}
service nova-api restart
service nova-cert restart
service nova-consoleauth restart
service nova-scheduler restart
service nova-conductor restart
service nova-novncproxy restart
{% endhighlight %}
7.2 安装配置计算节点
终于到了计算节点了
7.2.1 安装hypervisor
1 安装包 {% highlight sh %}
apt-get install nova-compute sysfsutils
{% endhighlight %}
2 编辑 /etc/nova/nova.conf 加入下面的内容
默认安装nova.conf内容好少,你要手动添加下面的内容。
{% highlight ini %}
[DEFAULT]
…
rpc_backend = rabbit
rabbit_host = controller
rabbit_password = openstack
auth_strategy = keystone
my_ip = 10.0.0.31
vnc_enabled = True vncserver_listen = 0.0.0.0 vncserver_proxyclient_address = 10.0.0.31 novncproxy_base_url = http://controller:6080/vnc_auto.html
verbose = True
[keystone_authtoken] … auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = nova admin_password = openstack
[glance] … host = controller {% endhighlight %}
7.2.2 完成安装
先看看这个节点支不支持硬件虚拟化 {% highlight sh %}
egrep -c ‘(vmx|svm)’ /proc/cpuinfo
{% endhighlight %}
如果返回的结果是0,那你就需要编辑/etc/nova/nova-compute.conf这个文件,把virt_type改成qemu:
{% highlight sh %} [libvirt] … virt_type = qemu {% endhighlight %}
重启计算服务 {% highlight sh %}
service nova-compute restart
{% endhighlight %}
7.3 验证安装
请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
1 切换为管理员 {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
2 列出所有的服务组件
{% highlight sh %}
$ nova service-list
+—-+——————+———–+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
| Id | Binary | Host | Zone | Status | State | Updated_at | Disabled Reason |
+—-+——————+———–+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
| 1 | nova-cert | localhost | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-12T10:04:04.000000 | - |
| 2 | nova-scheduler | localhost | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-12T10:04:12.000000 | - |
| 3 | nova-consoleauth | localhost | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-12T10:04:12.000000 | - |
| 4 | nova-conductor | localhost | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-12T10:04:11.000000 | - |
| 5 | nova-compute | localhost | nova | enabled | up | 2015-03-12T10:04:06.000000 | - |
+—-+——————+———–+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
{% endhighlight %}
Host那一列都是localhost有问题,我设置了hostname但是没有重启机器。重启以后应该会好。
3 列出所有映像
{% highlight sh %} $ nova image-list +————————————–+———————+——–+——–+ | ID | Name | Status | Server | +————————————–+———————+——–+——–+ | b460412b-4566-4d8b-8b9a-27f638f8ca58 | cirros-0.3.3-x86_64 | ACTIVE | | +————————————–+———————+——–+——–+ {% endhighlight %}
8 添加网络服务
OpenStack的网络服务是neutron,如果不安装neutron,nova-network也可以提供简单网络功能。neutron的功能更强大,所以我们使用neutron.
neutron应该是OpenStack最复杂的组件了。N多概念请参考OpenStack文档。我们在这里只验证它的安装过程。
8.1 安装配置控制节点
1 配置数据库 数据库安装在控制节点上。
{% highlight sh %} $ mysql -u root -p {% endhighlight %}
创建 neutron 数据库 {% highlight sql %} CREATE DATABASE neutron;
/* 用户名和密码都是neutron/openstack / GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON neutron. TO ’neutron’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON neutron.* TO ’neutron’@’%’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’; {% endhighlight %}
2 切换到管理员身份 {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
3 To create the service credentials, complete these steps:
创建 neutron 用户: {% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-create –name neutron –pass openstack +———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | email | | | enabled | True | | id | d9ea6a6733934f139a42dfad12f1009a | | name | neutron | | username | neutron | +———-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
为 neutron 用户添加admin角色:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone user-role-add –user neutron –tenant service –role admin
{% endhighlight %}
创建 neutron 服务实体:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone service-create –name neutron –type network
–description “OpenStack Networking”
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | OpenStack Networking |
| enabled | True |
| id | 8e45b333232e472c9bede063f71ffebb |
| name | neutron |
| type | network |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
创建计算服务API端点:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone endpoint-create
–service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ network / {print $2}’)
–publicurl http://controller:9696
–adminurl http://controller:9696
–internalurl http://controller:9696
–region regionOne
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| adminurl | http://controller:9696 |
| id | 0ec12e64cacf4eadac9421534b1d4028 |
| internalurl | http://controller:9696 |
| publicurl | http://controller:9696 |
| region | regionOne |
| service_id | 8e45b333232e472c9bede063f71ffebb |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
4 安装 neutron 包
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install neutron-server neutron-plugin-ml2 python-neutronclient
{% endhighlight %}
5 配置网络服务组件 编辑 /etc/neutron/neutron.conf 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] … rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack auth_strategy = keystone
core_plugin = ml2 service_plugins = router allow_overlapping_ips = True
notify_nova_on_port_status_changes = True notify_nova_on_port_data_changes = True nova_url = http://controller:8774/v2 nova_admin_auth_url = http://controller:35357/v2.0 nova_region_name = regionOne nova_admin_username = nova nova_admin_tenant_id = SERVICE_TENANT_ID nova_admin_password = openstack
verbose = True [keystone_authtoken]
#Comment out any auth_host, auth_port, and auth_protocol options because the identity_uri option replaces them. auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = neutron admin_password = openstack
[database] … connection = mysql://neutron:openstack@controller/neutron {% endhighlight %}
获得上述配置里的SERVICE_TENANT_ID
{% highlight sh %}
$ source admin-openrc.sh
$ keystone tenant-get service
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | Service Tenant |
| enabled | True |
| id | ef36de18149b4c809c4b26b63b6dda37 |
| name | service |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
6 配置 Modular Layer 2 (ML2) 插件
编辑 /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %} [ml2] … type_drivers = flat,gre tenant_network_types = gre mechanism_drivers = openvswitch
[ml2_type_gre] … tunnel_id_ranges = 1:1000
[securitygroup] … enable_security_group = True enable_ipset = True firewall_driver = neutron.agent.linux.iptables_firewall.OVSHybridIptablesFirewallDriver {% endhighlight %}
7 配置计算来使用网络
编辑 /etc/nova/nova.conf 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] … network_api_class = nova.network.neutronv2.api.API security_group_api = neutron linuxnet_interface_driver = nova.network.linux_net.LinuxOVSInterfaceDriver firewall_driver = nova.virt.firewall.NoopFirewallDriver
[neutron] … url = http://controller:9696 auth_strategy = keystone admin_auth_url = http://controller:35357/v2.0 admin_tenant_name = service admin_username = neutron admin_password = NEUTRON_PASS
{% endhighlight %}
8完成安装
装载neutron数据库:
{% highlight sh %}
su -s /bin/sh -c “neutron-db-manage –config-file /etc/neutron/neutron.conf
–config-file /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini upgrade juno” neutron
{% endhighlight %}
重启计算服务
{% highlight sh %}
service nova-api restart
service nova-scheduler restart
service nova-conductor restart
{% endhighlight %}
重启网络服务 {% highlight sh %}
service neutron-server restart
{% endhighlight %}
9 验证安装
{% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
列出已装载的扩展 {% highlight sh %} $ neutron ext-list +———————–+———————————————–+ | alias | name | +———————–+———————————————–+ | security-group | security-group | | l3_agent_scheduler | L3 Agent Scheduler | | ext-gw-mode | Neutron L3 Configurable external gateway mode | | binding | Port Binding | | provider | Provider Network | | agent | agent | | quotas | Quota management support | | dhcp_agent_scheduler | DHCP Agent Scheduler | | l3-ha | HA Router extension | | multi-provider | Multi Provider Network | | external-net | Neutron external network | | router | Neutron L3 Router | | allowed-address-pairs | Allowed Address Pairs | | extraroute | Neutron Extra Route | | extra_dhcp_opt | Neutron Extra DHCP opts | | dvr | Distributed Virtual Router | +———————–+———————————————–+
{% endhighlight %} 如果你运行这个命令是报下面的错误
unsupported locale setting
请设置LC_ALL为en_US.UTF-8 {% highlight sh %} export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 {% endhighlight %}
8.2 安装配置网络节点
8.2.1 准备工作
1 Edit the /etc/sysctl.conf file to contain the following parameters: {% highlight sh %} net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter=0 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter=0 {% endhighlight %}
2 应用它 {% highlight sh %}
sysctl -p
{% endhighlight %}
8.2.2 安装网络组件
{% highlight sh %}
# apt-get install neutron-plugin-ml2 neutron-plugin-openvswitch-agent
neutron-l3-agent neutron-dhcp-agent
{% endhighlight %}
8.2.3 配置网络公用组件
编辑 /etc/neutron/neutron.conf 加入下面的内容
- 注释掉所有的数据库连接的选项,因为neutron不直接连接数据库
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack
auth_strategy = keystone core_plugin = ml2 service_plugins = router allow_overlapping_ips = True verbose = True
[keystone_authtoken] #Comment out any auth_host, auth_port, and auth_protocol options because the identity_uri option replaces them. auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = neutron admin_password = openstack
{% endhighlight %}
8.2.3 配置Modular Layer 2 (ML2) 插件
编辑 /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %}
[ml2]
…
type_drivers = flat,gre
tenant_network_types = gre
mechanism_drivers = openvswitch
[ml2_type_flat] … flat_networks = external
[ml2_type_gre] … tunnel_id_ranges = 1:1000
[securitygroup] … enable_security_group = True enable_ipset = True firewall_driver = neutron.agent.linux.iptables_firewall.OVSHybridIptablesFirewallDriver
[ovs] … local_ip = INSTANCE_TUNNELS_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS enable_tunneling = True bridge_mappings = external:br-ex
[agent] … tunnel_types = gre {% endhighlight %}
INSTANCE_TUNNELS_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS 在本文中是 10.0.1.21
8.2.4 配置Layer-3 (L3) agent
编辑 /etc/neutron/l3_agent.ini 加入下面的内容
{% highlight sh %} [DEFAULT] … interface_driver = neutron.agent.linux.interface.OVSInterfaceDriver use_namespaces = True external_network_bridge = br-ex router_delete_namespaces = True … verbose = True {% endhighlight %}
8.2.5 配置DHCP agent
编辑 /etc/neutron/dhcp_agent.ini 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %}
[DEFAULT]
…
interface_driver = neutron.agent.linux.interface.OVSInterfaceDriver
dhcp_driver = neutron.agent.linux.dhcp.Dnsmasq
use_namespaces = True
dhcp_delete_namespaces = True
verbose = True
{% endhighlight %}
在官方手册里有一个可选的配置MTU的步骤,我们省略了.
8.2.6 配置metadata agent
编辑 /etc/neutron/metadata_agent.ini 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %}
[DEFAULT]
…
auth_url = http://controller:5000/v2.0
auth_region = regionOne
admin_tenant_name = service
admin_user = neutron
admin_password = NEUTRON_PASS
nova_metadata_ip = controller metadata_proxy_shared_secret = openstack verbose = True
{% endhighlight %}
- 在控制节点上
请注意下面的操作在控制节点上进行
编辑 /etc/nova/nova.conf 加入下面的内容
{% highlight sh %}
[DEFAULT]
service_metadata_proxy = True
metadata_proxy_shared_secret = openstack
{% endhighlight %}
重启计算API服务
{% highlight sh %}
service nova-api restart
{% endhighlight %}
8.2.7 配置Open vSwitch (OVS) 服务
下面的操作在网络节点上进行
{% highlight sh %}
service openvswitch-switch restart
ovs-vsctl add-br br-ex
ovs-vsctl add-port br-ex eth0
{% endhighlight %}
如果你的network节点只配置了1个NIC,那你就会无法连接到这台network节点上,除非你通过方式如XenServer的console。 请看我的在这一步遇到的问题。
8.2.8 完成安装
重启网络服务
{% highlight sh %}
service neutron-plugin-openvswitch-agent restart
service neutron-l3-agent restart
service neutron-dhcp-agent restart
service neutron-metadata-agent restart
{% endhighlight %}
8.2.8 验证安装
*请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
{% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh
#查询所有的代理 $ neutron agent-list
+————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+ | id | agent_type | host | alive | admin_state_up | binary | +————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+ | 02e5b551-197e-4fa3-8489-d19cb40e3171 | DHCP agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-dhcp-agent | | 6ea0949b-e389-437b-9be7-eb32bc138ef1 | Metadata agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-metadata-agent | | cd82006e-a82d-4576-a7fa-183f68b4ae73 | L3 agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-l3-agent | | fbfc1f77-bee0-413f-a38d-eff804cc573f | Open vSwitch agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent | +————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+
{% endhighlight %}
8.3 安装配置计算节点
计算节点处理实例的连接和安全规则组
8.3.1 准备工作
1 Edit the /etc/sysctl.conf file to contain the following parameters: {% highlight ini %} net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter=0 net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter=0 {% endhighlight %}
2 应用它 {% highlight sh %}
sysctl -p
{% endhighlight %}
8.3.2 安装网络组件
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install neutron-plugin-ml2 neutron-plugin-openvswitch-agent
{% endhighlight %}
8.3.3 配置网络公用组件
编辑 /etc/neutron/neutron.conf 这个文件
注释掉所有的数据库连接的选项,因为neutron不直接连接数据库
加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack
auth_strategy = keystone
core_plugin = ml2 service_plugins = router allow_overlapping_ips = True verbose = True
[keystone_authtoken] #Comment out any auth_host, auth_port, and auth_protocol options because the identity_uri option replaces them. auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = neutron admin_password = openstack
{% endhighlight %}
这个文件好像跟网络节点上的一模一样,:)
8.3.4 配置Modular Layer 2 (ML2) 插件
编辑 /etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini 加入下面的内容
{% highlight ini %}
[ml2]
…
type_drivers = flat,gre
tenant_network_types = gre
mechanism_drivers = openvswitch
[ml2_type_gre] … tunnel_id_ranges = 1:1000
[securitygroup] … enable_security_group = True enable_ipset = True firewall_driver = neutron.agent.linux.iptables_firewall.OVSHybridIptablesFirewallDriver
[ovs] … local_ip = INSTANCE_TUNNELS_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS enable_tunneling = True bridge_mappings = external:br-ex
[agent] … tunnel_types = gre {% endhighlight %}
INSTANCE_TUNNELS_INTERFACE_IP_ADDRESS这个IP应该是计算节点的tunnel IP:10.0.1.31
8.3.5 配置Open vSwitch (OVS)服务
{% highlight sh %}
service openvswitch-switch restart
{% endhighlight %}
8.3.6 配置计算来使用网络
默认安装包使用的是 legacy networking,也就nova-network。你必须重新配置计算节点使用neutron来管理网络。
编辑 /etc/nova/nova.conf 加入以下内容:
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT]
注意: 默认计算组件nova使用了一个内部实现的防火墙服务,因为网络组件neutron包含了防火墙服务,所以你必须把nova的内部防火墙服务禁用,做法是设置firewall_driver = nova.virt.firewall.NoopFirewallDriver.
network_api_class = nova.network.neutronv2.api.API security_group_api = neutron linuxnet_interface_driver = nova.network.linux_net.LinuxOVSInterfaceDriver firewall_driver = nova.virt.firewall.NoopFirewallDriver
[neutron] … url = http://controller:9696 auth_strategy = keystone admin_auth_url = http://controller:35357/v2.0 admin_tenant_name = service admin_username = neutron admin_password = openstack {% endhighlight %}
8.3.7 完成安装
{% highlight sh %}
service nova-compute restart
service neutron-plugin-openvswitch-agent restart
{% endhighlight %}
8.3.8 验证安装
*请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
{% highlight sh %}
$ source admin-openrc.sh
$ neutron agent-list
+————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+
| id | agent_type | host | alive | admin_state_up | binary |
+————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+
| 02e5b551-197e-4fa3-8489-d19cb40e3171 | DHCP agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-dhcp-agent |
| 6ea0949b-e389-437b-9be7-eb32bc138ef1 | Metadata agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-metadata-agent |
| cd82006e-a82d-4576-a7fa-183f68b4ae73 | L3 agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-l3-agent |
| e3fe92b0-afee-49e3-a783-e5900182fd5b | Open vSwitch agent | compute1 | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
| fbfc1f77-bee0-413f-a38d-eff804cc573f | Open vSwitch agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
+————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+
{% endhighlight %}
可以看到在host列有compute1,也就是计算节点上的Open vSwitch agent已启动。
8.4 创建初始网络
在启动虚拟机之前,你要先创建虚拟网络基本架构,实例会连接到它上。这个虚拟网络包含一个外部网络和租户网络。
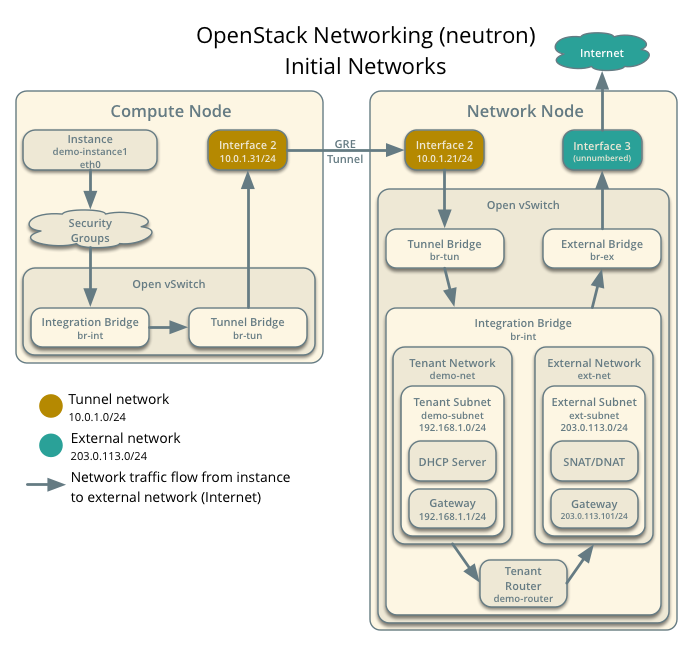
8.4.1 外部网络
外部网络向实例提供互联网访问支持。默认它允许实例以Network Address Translation (NAT)方式访问互联网。 使用浮动IP和适当安全规则组,你可以使单个实例访问Internet。管理员租户会拥有这个网络,因为它向所有的租户提供外部网络。
注意 请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
1 创建外部网络
{% highlight sh %}
source admin-openrc.sh
$ neutron net-create ext-net –router:external True
–provider:physical_network external –provider:network_type flat
Created a new network:
+—————————+————————————–+
| Field | Value |
+—————————+————————————–+
| admin_state_up | True |
| id | c3b0a6f6-7bed-4058-9a20-1f33396e331f |
| name | ext-net |
| provider:network_type | flat |
| provider:physical_network | external |
| provider:segmentation_id | |
| router:external | True |
| shared | False |
| status | ACTIVE |
| subnets | |
| tenant_id | 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 |
+—————————+————————————–+
{% endhighlight %}
我们创建的这个外网,它跟网络节点的那个绑定外网地址的网卡在一个子网,共享网关。 跟物理网一样,我们需要给它创建一个子网。
2 在外网上创建子网
创建的命令如下:
{% highlight sh %}
$ neutron subnet-create ext-net –name ext-subnet
–allocation-pool start=FLOATING_IP_START,end=FLOATING_IP_END
–disable-dhcp –gateway EXTERNAL_NETWORK_GATEWAY EXTERNAL_NETWORK_CIDR
{% endhighlight %}
本文是外网的网段是192.168.234.0/24 ,我们分配浮动IP段为234.230~234.239
{% highlight sh %}
$ neutron subnet-create ext-net –name ext-subnet
–allocation-pool start=192.168.234.230,end=192.168.234.239
–disable-dhcp –gateway 192.168.234.1 192.168.234.0/24
Created a new subnet: +——————-+——————————————————–+ | Field | Value | +——————-+——————————————————–+ | allocation_pools | {“start”: “192.168.234.230”, “end”: “192.168.234.239”} | | cidr | 192.168.234.0/24 | | dns_nameservers | | | enable_dhcp | False | | gateway_ip | 192.168.234.1 | | host_routes | | | id | 33bc7923-789c-4453-9dd2-7853b4c69c5c | | ip_version | 4 | | ipv6_address_mode | | | ipv6_ra_mode | | | name | ext-subnet | | network_id | c3b0a6f6-7bed-4058-9a20-1f33396e331f | | tenant_id | 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 | +——————-+——————————————————–+ {% endhighlight %}
8.4.2 租户网络
The tenant network provides internal network access for instances. The architecture isolates this type of network from other tenants. The demo tenant owns this network because it only provides network access for instances within it.
注意 请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
1 创建租户网络
{% highlight sh %}
source demo-openrc.sh
$ neutron net-create demo-net
Created a new network: +—————–+————————————–+ | Field | Value | +—————–+————————————–+ | admin_state_up | True | | id | dba2bba4-c2a5-410a-9b6f-da8a1e9b887f | | name | demo-net | | router:external | False | | shared | False | | status | ACTIVE | | subnets | | | tenant_id | 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 | +—————–+————————————–+ {% endhighlight %}
2 在租户网络上创建子网
{% highlight sh %}
$ neutron subnet-create demo-net –name demo-subnet
–gateway 10.10.1.1 10.10.1.0/24
Created a new subnet: +——————-+———————————————-+ | Field | Value | +——————-+———————————————-+ | allocation_pools | {“start”: “10.10.1.2”, “end”: “10.10.1.254”} | | cidr | 10.10.1.0/24 | | dns_nameservers | | | enable_dhcp | True | | gateway_ip | 10.10.1.1 | | host_routes | | | id | e07e263f-1cf8-4f60-adbb-424fbd22ed0d | | ip_version | 4 | | ipv6_address_mode | | | ipv6_ra_mode | | | name | demo-subnet | | network_id | dba2bba4-c2a5-410a-9b6f-da8a1e9b887f | | tenant_id | 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 | +——————-+———————————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
3 创建路由器 路由器用来连接租户网络和外部网络
创建路由器
{% highlight sh %} $ neutron router-create demo-router
Created a new router: +———————–+————————————–+ | Field | Value | +———————–+————————————–+ | admin_state_up | True | | external_gateway_info | | | id | 979f88e6-65e2-4d97-b468-4b1e95687da4 | | name | demo-router | | routes | | | status | ACTIVE | | tenant_id | 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 | +———————–+————————————–+
{% endhighlight %}
把它加到租户网络内 {% highlight sh %} $ neutron router-interface-add demo-router demo-subnet Added interface 2e55f3dc-763f-4031-8011-b2b2dd9df5fe to router demo-router. {% endhighlight %} 设置路由器的网关使它连接到外网 {% highlight sh %} $ neutron router-gateway-set demo-router ext-net Set gateway for router demo-router {% endhighlight %}
8.5 验证安装
如果你的安装没问题,那么租户的路由会占用最低的那个IP:192.168.234.230,你在外网的任何一台机器上应该能ping通它。
9 安装控制台
The OpenStack dashboard, also known as Horizon,是它的web管理界面。
9.1 安装配置Horizon
我们把Horizon安装在控制节点上
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install openstack-dashboard apache2 libapache2-mod-wsgi memcached python-memcache
{% endhighlight %}
配置Horizon
编辑它 /etc/openstack-dashboard/local_settings.py 加入下面的内容。
{% highlight py %} OPENSTACK_HOST = “controller” ALLOWED_HOSTS = [’*’] CACHES = { ‘default’: { ‘BACKEND’: ‘django.core.cache.backends.memcached.MemcachedCache’, ‘LOCATION’: ‘127.0.0.1:11211’, } } TIME_ZONE = “Asia/Shanghai” {% endhighlight %}
3 完成安装
{% highlight sh %}
service apache2 restart
service memcached restart
{% endhighlight %}
9.2 验证安装
在浏览器里输入:http://controller/horizon,来访问Horizon。
10 安装Telemetry
Telemetry的组件信息请参考官方文档
10. 1 安装配置控制节点
10.1.1 配置先决条件
1 安装 MongoDB
{% highlight aconf %}
apt-get install mongodb-server mongodb-clients python-pymongo
{% endhighlight %}
2 编辑 /etc/mongodb.conf file 完成下列操作:
{% highlight aconf %} bind_ip = 10.0.0.11 smallfiles = true {% endhighlight %}
执行命令 {% highlight sh %}
service mongodb stop
rm /var/lib/mongodb/journal/prealloc.*
service mongodb start
{% endhighlight %}
3 创建 ceilometer 数据库
{% highlight sh %}
mongo –host controller –eval '
db = db.getSiblingDB(“ceilometer”); db.addUser({user: “ceilometer”, pwd: “openstack”, roles: [ “readWrite”, “dbAdmin” ]})’
MongoDB shell version: 2.4.9 connecting to: controller:27017/test { “user” : “ceilometer”, “pwd” : “347ed5cbd578cb16ce413fe1d085ce2f”, “roles” : [ “readWrite”, “dbAdmin” ], “_id” : ObjectId(“550a3f247f38cb43ba640fd7”) } {% endhighlight %}
4 切换到管理员身份 {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
5 创建 ceilometer 用户
{% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-create –name ceilometer –pass openstack +———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | email | | | enabled | True | | id | d839485477e44aa8baabbefd19829392 | | name | ceilometer | | username | ceilometer | +———-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
为 ceilometer 用户添加admin角色: {% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-role-add –user ceilometer –tenant service –role admin {% endhighlight %}
创建 ceilometer 服务实体:
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone service-create –name ceilometer –type metering
–description “Telemetry”
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | Telemetry |
| enabled | True |
| id | 92a5e6518c1d4b238f66c1358d472196 |
| name | ceilometer |
| type | metering |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
创建 Telemetry API endpoints
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone endpoint-create
–service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ metering / {print $2}’)
–publicurl http://controller:8777
–internalurl http://controller:8777
–adminurl http://controller:8777
–region regionOne
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| adminurl | http://controller:8777 |
| id | f513c95f58a54d028c67db8e9d8e1e20 |
| internalurl | http://controller:8777 |
| publicurl | http://controller:8777 |
| region | regionOne |
| service_id | 92a5e6518c1d4b238f66c1358d472196 |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
10.1.2 配置先决条件
1 安装包
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install ceilometer-api ceilometer-collector ceilometer-agent-central \
ceilometer-agent-notification ceilometer-alarm-evaluator ceilometer-alarm-notifier
python-ceilometerclient
{% endhighlight %}
2 生成一个随机密码 {% highlight sh %}
openssl rand -hex 10
177e8037fc8c7916e329 {% endhighlight %}
3 编辑 /etc/ceilometer/ceilometer.conf 完成下列操作: {% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] … rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack … auth_strategy = keystone verbose = True
[keystone_authtoken] #Comment out any auth_host, auth_port, and auth_protocol options because the identity_uri option replaces them. auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = ceilometer admin_password = openstack
[database] … connection = mongodb://ceilometer:openstack@controller:27017/ceilometer
[service_credentials] … os_auth_url = http://controller:5000/v2.0 os_username = ceilometer os_tenant_name = service os_password = openstack
[publisher] … metering_secret = METERING_SECRET {% endhighlight %}
把METERING_SECRET替换成我们上一步创建的177e8037fc8c7916e329
4 完成安装
重启服务
{% highlight sh %}
service ceilometer-agent-central restart
service ceilometer-agent-notification restart
service ceilometer-api restart
service ceilometer-collector restart
service ceilometer-alarm-evaluator restart
service ceilometer-alarm-notifier restart
{% endhighlight %}
10.2 安装配置计算节点
Telemetry 使用通知和代理的组合来收集计算节点的计费信息,请在每个计算节点上执行下列操作.
10.2.1 安装配置Agent
1 {% highlight sh %}
apt-get install ceilometer-agent-compute
{% endhighlight %}
2 编辑 /etc/ceilometer/ceilometer.conf 完成下列操作: {% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] … rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack verbose = True
[publisher] … metering_secret = METERING_SECRET
[keystone_authtoken] #Comment out any auth_host, auth_port, and auth_protocol options because the identity_uri option replaces them. auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = ceilometer admin_password = openstack
[service_credentials] … os_auth_url = http://controller:5000/v2.0 os_username = ceilometer os_tenant_name = service os_password = openstack os_endpoint_type = internalURL os_region_name = regionOne
{% endhighlight %}
把METERING_SECRET替换成我们上一步创建的177e8037fc8c7916e329
10.2.2 安装配置通知
Edit the /etc/nova/nova.conf file and configure notifications in the [DEFAULT] section:
编辑 /etc/nova/nova.conf ,配置在 [DEFAULT] 小节配置通知:
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] instance_usage_audit = True instance_usage_audit_period = hour notify_on_state_change = vm_and_task_state notification_driver = messagingv2 {% endhighlight %}
10.2.3 完成安装
{% highlight sh %}
service ceilometer-agent-compute restart
service nova-compute restart
{% endhighlight %}
10.2 安装配置映像服务
请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
编辑文件 /etc/glance/glance-api.conf 和 /etc/glance/glance-registry.conf 完成下面所提的操作:
{% highlight sh %} [DEFAULT] … notification_driver = messagingv2 rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack {% endhighlight %}
重启服务
{% highlight sh %}
service glance-registry restart
service glance-api restart
{% endhighlight %}
11 安装过程中遇到的问题
11.1 服务状态不对
安装的时候没有把控制节点的hostname改成controller,改完后发现有状态为down的服务
{% highlight sh %} root@localhost:~# nova service-list +—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+ | Id | Binary | Host | Zone | Status | State | Updated_at | Disabled Reason | +—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+ | 1 | nova-cert | localhost | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-17T09:40:43.000000 | - | | 2 | nova-scheduler | localhost | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-17T09:40:50.000000 | - | | 3 | nova-consoleauth | localhost | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-17T09:40:50.000000 | - | | 4 | nova-conductor | localhost | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-17T09:41:04.000000 | - | | 6 | nova-compute | compute1 | nova | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:42:37.000000 | - | | 7 | nova-cert | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:42:43.000000 | - | | 8 | nova-scheduler | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:42:38.000000 | - | | 9 | nova-consoleauth | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:42:38.000000 | - | | 10 | nova-conductor | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:42:41.000000 | - | +—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+ {% endhighlight %}
如果运行上述命令是报unsupported locale setting错误,请设置环境变量
{% highlight sh %}
export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
{% endhighlight %}
把那些状态为down的服务删除。
{% highlight sh %}
root@localhost:# nova service-delete 1
root@localhost:# nova service-delete 2
root@localhost:# nova service-delete 3
root@localhost:# nova service-delete 4
root@localhost:~# nova service-list
+—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
| Id | Binary | Host | Zone | Status | State | Updated_at | Disabled Reason |
+—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
| 6 | nova-compute | compute1 | nova | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:43:57.000000 | - |
| 7 | nova-cert | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:44:03.000000 | - |
| 8 | nova-scheduler | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:43:58.000000 | - |
| 9 | nova-consoleauth | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:43:58.000000 | - |
| 10 | nova-conductor | controller | internal | enabled | up | 2015-03-17T09:44:02.000000 | - |
+—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
{% endhighlight %}
因为我在安装的过程中网络节点重装过,所以也出现了类似的情况。
{% highlight sh %}
root@localhost:# neutron agent-list
+————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+
| id | agent_type | host | alive | admin_state_up | binary |
+————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+
| 02e5b551-197e-4fa3-8489-d19cb40e3171 | DHCP agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-dhcp-agent |
| 6ea0949b-e389-437b-9be7-eb32bc138ef1 | Metadata agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-metadata-agent |
| 77b4f1ad-4dc4-4a00-881f-6709b63c856a | Open vSwitch agent | localhost | xxx | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
| 809776b5-42f0-4c5c-afee-1e8fc1877be9 | DHCP agent | localhost | xxx | True | neutron-dhcp-agent |
| aeadc622-155c-46c5-bd2b-f75f715664ca | Metadata agent | localhost | xxx | True | neutron-metadata-agent |
| b18cf8ae-3893-436f-beef-315274d837b2 | L3 agent | localhost | xxx | True | neutron-l3-agent |
| cd82006e-a82d-4576-a7fa-183f68b4ae73 | L3 agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-l3-agent |
| e3fe92b0-afee-49e3-a783-e5900182fd5b | Open vSwitch agent | compute1 | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
| fbfc1f77-bee0-413f-a38d-eff804cc573f | Open vSwitch agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
+————————————–+——————–+———–+——-+—————-+—————————+
root@localhost:# neutron agent-delete 77b4f1ad-4dc4-4a00-881f-6709b63c856a
Deleted agent: 77b4f1ad-4dc4-4a00-881f-6709b63c856a
root@localhost:# neutron agent-delete 809776b5-42f0-4c5c-afee-1e8fc1877be9
Deleted agent: 809776b5-42f0-4c5c-afee-1e8fc1877be9
root@localhost:# neutron agent-delete aeadc622-155c-46c5-bd2b-f75f715664ca
Deleted agent: aeadc622-155c-46c5-bd2b-f75f715664ca
root@localhost:# neutron agent-delete b18cf8ae-3893-436f-beef-315274d837b2
Deleted agent: b18cf8ae-3893-436f-beef-315274d837b2
root@localhost:# neutron agent-list
+————————————–+——————–+———-+——-+—————-+—————————+
| id | agent_type | host | alive | admin_state_up | binary |
+————————————–+——————–+———-+——-+—————-+—————————+
| 02e5b551-197e-4fa3-8489-d19cb40e3171 | DHCP agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-dhcp-agent |
| 6ea0949b-e389-437b-9be7-eb32bc138ef1 | Metadata agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-metadata-agent |
| cd82006e-a82d-4576-a7fa-183f68b4ae73 | L3 agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-l3-agent |
| e3fe92b0-afee-49e3-a783-e5900182fd5b | Open vSwitch agent | compute1 | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
| fbfc1f77-bee0-413f-a38d-eff804cc573f | Open vSwitch agent | network | :-) | True | neutron-openvswitch-agent |
+————————————–+——————–+———-+——-+—————-+—————————+
{% endhighlight %}
11.2 启动实例时报错
{% highlight sh %} Build of instance 84c2c847-bcc7-4fad-8e81-4430b156cc46 aborted: Failed to allocate the network(s), not rescheduling. {% endhighlight %}
查看网络节点的日志,发现报错: {% highlight sh %} neutron ImportError: No module named rabbit {% endhighlight %}
网上说这是OpenStack上一个版本Icehouse的问题,我忽然意识到我在安装新的网络节点时,没有导入新的源,Ubuntu 14.04的官方源里还真就是Icehouse版本。 {% highlight sh %}
apt-get install ubuntu-cloud-keyring
echo “deb http://ubuntu-cloud.archive.canonical.com/ubuntu" \
“trusty-updates/juno main” > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cloudarchive-juno.list {% endhighlight %} 导入上面的源重新安装了包,启动服务后,不报这个错误了。
不过主机还是没启动起来。。。。 还是报Failed to allocate the network(s), not rescheduling.错误。
查看计算节点compute1上的/var/log/neutron/openvswitch-agent.log,发现如下错误: {% highlight sh %} Bridge br-ex for physical network external does not exist. Agent terminated! {% endhighlight %}
仔细查看计算节点上的/etc/neutron/plugins/ml2/ml2_conf.ini 时发现里面有这个bridge_mappings = external:br-ex选项,官方安装文档里没有提这个选项,禁用它试试。
{% highlight ini %} #bridge_mappings = external:br-ex {% endhighlight %} 嗯,不报上面的错误了。
不过云主机还是启动不起来,还是报Failed to allocate the network(s), not rescheduling。
查看计算节点compute1上的/var/log/nova/nova-compute.log发现这个错误 {% highlight sh %} VirtualInterfaceCreateException: Virtual Interface creation failed {% endhighlight %}
这个帖子解决了我的问题,在计算节点的nova.conf里加入
{% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] #加入下面两行 vif_plugging_is_fatal: false vif_plugging_timeout: 0 {% endhighlight %}
实例终于启动起来了。
在我启动控制节点后, {% highlight sh %}
nova service-list
+—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+ | Id | Binary | Host | Zone | Status | State | Updated_at | Disabled Reason | +—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+ | 6 | nova-compute | compute1 | nova | enabled | down | 2015-03-18T09:33:33.000000 | - | | 7 | nova-cert | controller | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-18T09:33:26.000000 | - | | 8 | nova-scheduler | controller | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-18T09:33:28.000000 | - | | 9 | nova-consoleauth | controller | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-18T09:33:28.000000 | - | | 10 | nova-conductor | controller | internal | enabled | down | 2015-03-18T09:33:28.000000 | - | +—-+——————+————+———-+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+ {% endhighlight %} 这几个服务的日志报的都是这个错误: {% highlight sh %} AMQP server controller:5672 closed the connection. Check login credentials: Socket closed {% endhighlight %}
我傻乎乎的重启了N遍服务,还怀疑是iptables的问题。其它错误里说得挺清楚的:Check login credentials。不过我真没想到重启会让guest的密码失效。重新设置一下这个密码就OK了。 {% highlight sh %} rabbitmqctl change_password guest openstack {% endhighlight %}
- 如何设置ceilometer的轮询间隔
https://ask.openstack.org/en/question/5882/how-to-change-the-polling-period-of-ceilometer/
启动实例的
apache的错误日志显示:
{% highlight sh %} [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200854 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] Internal Server Error: /horizon/project/instances/launch [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200922 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] Traceback (most recent call last): [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200931 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/core/handlers/base.py”, line 112, in get_response [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200939 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] response = wrapped_callback(request, *callback_args, **callback_kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200945 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/decorators.py”, line 36, in dec [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200952 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return view_func(request, *args, **kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200958 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/decorators.py”, line 52, in dec [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200964 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return view_func(request, *args, **kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200970 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/decorators.py”, line 36, in dec [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200977 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return view_func(request, *args, **kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200983 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/decorators.py”, line 84, in dec [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200989 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return view_func(request, *args, **kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.200995 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/views/generic/base.py”, line 69, in view [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201002 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201008 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/views/generic/base.py”, line 87, in dispatch [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201014 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return handler(request, *args, **kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201020 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/workflows/views.py”, line 165, in post [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201027 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] context = self.get_context_data(**kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201033 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/workflows/views.py”, line 89, in get_context_data [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201039 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] workflow = self.get_workflow() [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201045 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/workflows/views.py”, line 79, in get_workflow [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201051 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] entry_point=entry_point) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201069 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/workflows/base.py”, line 648, in init [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201075 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] valid = step.action.is_valid() [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201081 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/forms/forms.py”, line 129, in is_valid [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201086 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return self.is_bound and not bool(self.errors) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201092 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/forms/forms.py”, line 121, in errors [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201097 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] self.full_clean() [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201103 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/forms/forms.py”, line 274, in full_clean [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201108 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] self._clean_form() [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201113 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/django/forms/forms.py”, line 300, in _clean_form [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201119 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] self.cleaned_data = self.clean() [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201124 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/share/openstack-dashboard/openstack_dashboard/wsgi/../../openstack_dashboard/dashboards/project/instances/workflows/create_instance.py”, line 167, in clean [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201131 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] usages = quotas.tenant_quota_usages(self.request) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201136 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/horizon/utils/memoized.py”, line 90, in wrapped [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201142 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] value = cache[key] = func(*args, **kwargs) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201148 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/share/openstack-dashboard/openstack_dashboard/wsgi/../../openstack_dashboard/usage/quotas.py”, line 224, in tenant_quota_usages [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201153 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] disabled_quotas=disabled_quotas): [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201159 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/share/openstack-dashboard/openstack_dashboard/wsgi/../../openstack_dashboard/usage/quotas.py”, line 165, in get_tenant_quota_data [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201165 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] tenant_id=tenant_id) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201171 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/share/openstack-dashboard/openstack_dashboard/wsgi/../../openstack_dashboard/usage/quotas.py”, line 147, in _get_quota_data [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201177 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] quotasets.append(getattr(cinder, method_name)(request, tenant_id)) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201182 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/share/openstack-dashboard/openstack_dashboard/wsgi/../../openstack_dashboard/api/cinder.py”, line 363, in tenant_quota_get [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201188 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return base.QuotaSet(c_client.quotas.get(tenant_id)) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201193 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/cinderclient/v1/quotas.py”, line 39, in get [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201199 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] “quota_set”) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201204 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/cinderclient/base.py”, line 151, in _get [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201209 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] return self.resource_class(self, body[response_key], loaded=True) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201215 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/cinderclient/openstack/common/apiclient/base.py”, line 429, in init [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201227 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] self._add_details(info) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201233 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/cinderclient/openstack/common/apiclient/base.py”, line 450, in _add_details [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201238 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] setattr(self, k, v) [Tue Mar 24 17:31:32.201244 2015] [:error] [pid 23314:tid 140209584568064] UnicodeEncodeError: ‘ascii’ codec can’t encode characters in position 10-11: ordinal not in range(128) {% endhighlight %}
在看了python对unicode的支持后,修改了源代码 “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/cinderclient/openstack/common/apiclient/base.py” {% highlight python %} setattr(self, k.encode(‘UTF-8’), v.encode(‘UTF-8’)) #setattr(self, k, v) {% endhighlight %} 可以了.
12 安装块存储设备
12.1 安装配置控制节点
12.1.1 安装准备
- 配置数据库 数据库安装在控制节点上。
{% highlight sh %} $ mysql -u root -p {% endhighlight %}
创建 cinder 数据库 {% highlight sql %} CREATE DATABASE cinder;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON cinder.* TO ‘cinder’@’localhost’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON cinder.* TO ‘cinder’@’%’
IDENTIFIED BY ‘openstack’;
{% endhighlight %}
用切换到管理员身份 {% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
创建服务凭证
创建 cinder 用户
{% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-create –name cinder –pass openstack +———-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———-+———————————-+ | email | | | enabled | True | | id | fd7b1e90d1144b669d20040b9c334d88 | | name | cinder | | username | cinder | +———-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
为 cinder 用户添加admin角色: {% highlight sh %} $ keystone user-role-add –user cinder –tenant service –role admin {% endhighlight %}
创建 cinder 服务实体:
注意 块存储服务需要两个不同的实体以支持v1和v2版本的API.
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone service-create –name cinder –type volume
–description “OpenStack Block Storage”
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | OpenStack Block Storage |
| enabled | True |
| id | c6a863efddac421cbb6e1585ae0c026d |
| name | cinder |
| type | volume |
+————-+———————————-+
$ keystone service-create –name cinderv2 –type volumev2
–description “OpenStack Block Storage”
+————-+———————————-+
| Property | Value |
+————-+———————————-+
| description | OpenStack Block Storage |
| enabled | True |
| id | 61c641af06544f8eb74a99f4c30b65ee |
| name | cinderv2 |
| type | volumev2 |
+————-+———————————-+
{% endhighlight %}
创建块存储服务 API 端点:
当然也是两个
{% highlight sh %}
$ keystone endpoint-create
–service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ volume / {print $2}’)
–publicurl http://controller:8776/v1/%(tenant_id)s
–internalurl http://controller:8776/v1/%(tenant_id)s
–adminurl http://controller:8776/v1/%(tenant_id)s
–region regionOne
+————-+—————————————–+
| Property | Value |
+————-+—————————————–+
| adminurl | http://controller:8776/v1/%(tenant_id)s |
| id | 1dadfd1345034f5bbec0a37fbb362e9c |
| internalurl | http://controller:8776/v1/%(tenant_id)s |
| publicurl | http://controller:8776/v1/%(tenant_id)s |
| region | regionOne |
| service_id | c6a863efddac421cbb6e1585ae0c026d |
+————-+—————————————–+
$ keystone endpoint-create
–service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ volumev2 / {print $2}’)
–publicurl http://controller:8776/v2/%(tenant_id)s
–internalurl http://controller:8776/v2/%(tenant_id)s
–adminurl http://controller:8776/v2/%(tenant_id)s
–region regionOne
+————-+—————————————–+
| Property | Value |
+————-+—————————————–+
| adminurl | http://controller:8776/v2/%(tenant_id)s |
| id | 8e40819ec3174b52a0d553d5fdec5a98 |
| internalurl | http://controller:8776/v2/%(tenant_id)s |
| publicurl | http://controller:8776/v2/%(tenant_id)s |
| region | regionOne |
| service_id | 61c641af06544f8eb74a99f4c30b65ee |
+————-+—————————————–+
{% endhighlight %}
12.1.2 安装配置存储控制组件
1 安装包
{% highlight sh %}
apt-get install cinder-api cinder-scheduler python-cinderclient
{% endhighlight %}
2 编辑 /etc/cinder/cinder.conf 完成下列操作: {% highlight ini %} [database] … connection = mysql://cinder:openstack@controller/cinder
[DEFAULT] … rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack
my_ip = 10.0.0.11
verbose = True
… auth_strategy = keystone
[keystone_authtoken] … #Comment out any auth_host, auth_port, and auth_protocol options because the identity_uri option replaces them.
auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = cinder admin_password = openstack
{% endhighlight %}
3 组装数据库
{% highlight sh %}
su -s /bin/sh -c “cinder-manage db sync” cinder
{% endhighlight %}
12.1.3 完成安装
重启服务
{% highlight sh %}
service cinder-scheduler restart
service cinder-api restart
{% endhighlight %}
删除没用的sqlite文件. {% highlight sh %}
rm -f /var/lib/cinder/cinder.sqlite
{% endhighlight %}
12.2 安装配置一个存储节点
12.2.1 To configure prerequisites
需要一台新的虚拟机,当然你要配置安装Ubuntu Cloud的keyring和仓库,配置时间同步,请参考 基础环境 那一节
设置hostname为block1
配置管理IP
{% highlight sh %}
The primary network interface
auto eth0 iface eth0 inet static address 192.168.234.206 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.234.1
management interface
auto eth0:1 iface eth0:1 inet static address 10.0.0.41 netmask 255.255.255.0 {% endhighlight %}
配置 /etc/hosts 加入下面内容
{% highlight sh %}
block1
10.0.0.41 block1 {% endhighlight %}
其它的三个节点的hosts文件里也要加入这一行.
安装lvm包
{% highlight sh %}
aptitude install lvm2 -y
{% endhighlight %}
我为这个存储节点添加了一块新的虚拟硬盘,可以用fdisk查看一下 {% highlight sh %}
fdisk -l
Disk /dev/xvda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders, total 20971520 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x000db5b8
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/xvda1 2048 499711 248832 83 Linux /dev/xvda2 501758 20969471 10233857 5 Extended /dev/xvda5 501760 20969471 10233856 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/xvdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders, total 41943040 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/xvdb doesn’t contain a valid partition table
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-root: 9944 MB, 9944694784 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1209 cylinders, total 19423232 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-root doesn’t contain a valid partition table
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-swap_1: 532 MB, 532676608 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 64 cylinders, total 1040384 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-swap_1 doesn’t contain a valid partition table
{% endhighlight %}
可以看到新加的disk没有分区,我们来把它分成lvm的分区,具体请参考我的这篇blog. 分区完成后我们再看看分区表
{% highlight sh %}
fdisk -l
Disk /dev/xvda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders, total 20971520 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x000db5b8
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/xvda1 2048 499711 248832 83 Linux /dev/xvda2 501758 20969471 10233857 5 Extended /dev/xvda5 501760 20969471 10233856 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/xvdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes 213 heads, 34 sectors/track, 5791 cylinders, total 41943040 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x38c87633
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/xvdb1 2048 41943039 20970496 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-root: 9944 MB, 9944694784 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1209 cylinders, total 19423232 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-root doesn’t contain a valid partition table
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-swap_1: 532 MB, 532676608 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 64 cylinders, total 1040384 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0x00000000
Disk /dev/mapper/ubuntu1404server–vg-swap_1 doesn’t contain a valid partition table
{% endhighlight %}
/dev/xvdb1 已经是lvm的了,用它创建一个物理卷.
{% highlight sh %}
pvcreate /dev/xvdb1
Physical volume “/dev/xvdb1” successfully created
{% endhighlight %}
这样我们就创建了一个物理卷,名叫/dev/xvdb1,跟它的设备名是一样的.
创建一个卷组(Volume Group),这个物理加到这个卷组中. {% highlight sh %}
vgcreate cinder-volumes /dev/xvdb1
Volume group “cinder-volumes” successfully created {% endhighlight %}
cinder-volumes是cinder默认使用的卷组,如果你的卷组不叫这个也没关系,可以在cinder.conf中修改.
创建完卷组就OK了,创建逻辑卷的工作就交给OpenStack了.
有一项非常重要的工作要做.
默认的lvm卷扫描工具会扫描 /dev目录来查看包含逻辑卷的设备,如果tenant创建了一个lvm的卷的话,那存储节点上的lvm会发现并缓存他们,会导致存储节点和tenant的主机都有问题.所以我们要限制lvm只扫描包含"cinder-volumes"的设备
编辑 /etc/lvm/lvm.conf
{% highlight ini %}
devices {
…
filter = [ “a/xvda/”,“a/xvdb/”, “r/.*/”]
{% endhighlight %}
我为什么会把"a/xvda/“这个加到过滤器里,是因为我的节点的操作系统ubuntu是装在lvm上的,所以我必须允许lvm扫描这个设备.
你可以使用vgs -vvvv来测试你的过滤器.
如果你的计算节点也使用了lvm,你也要同时设置扫描过滤器.
12.2.2 安装包
1 {% highlight sh %}
apt-get install cinder-volume python-mysqldb
{% endhighlight %}
编辑 /etc/cinder/cinder.conf 完成下列操作: {% highlight ini %} [DEFAULT] … rpc_backend = rabbit rabbit_host = controller rabbit_password = openstack
my_ip = 10.0.0.41 glance_host = controller verbose = True auth_strategy = keystone
[keystone_authtoken] … auth_uri = http://controller:5000/v2.0 identity_uri = http://controller:35357 admin_tenant_name = service admin_user = cinder admin_password = openstack
[database] … connection = mysql://cinder:openstack@controller/cinder
{% endhighlight %}
12.2.3 完成安装
{% highlight sh %}
service tgt restart
service cinder-volume restart
rm -f /var/lib/cinder/cinder.sqlite
{% endhighlight %}
12.3 验证安装
请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
{% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
{% highlight sh %}
cinder service-list
+——————+————+——+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
| Binary | Host | Zone | Status | State | Updated_at | Disabled Reason |
+——————+————+——+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
| cinder-scheduler | controller | nova | enabled | up | 2015-03-20T03:46:57.000000 | None |
| cinder-volume | block1 | nova | enabled | up | 2015-03-20T03:46:53.000000 | None |
+——————+————+——+———+——-+—————————-+—————–+
{% endhighlight %}
切换成demo租户 {% highlight sh %} $ source demo-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
创建一个卷 {% highlight sh %} $ cinder create –display-name demo-volume1 1 {% endhighlight %}
查看这个新建的卷
{% highlight sh %} $ cinder list {% endhighlight %}
13 启用EC2兼容API
请在控制节点上运行下面的命令
{% highlight sh %} $ source admin-openrc.sh {% endhighlight %}
1 创建EC2的服务
{% highlight sh %}
# keystone service-create –name=ec2
–type=ec2
–description=“EC2 Compatibility Layer”
+————-+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +————-+———————————-+ | description | EC2 Compatibility Layer | | enabled | True | | id | a18a1b887b484ed6a1130174ccb8eb5f | | name | ec2 | | type | ec2 | +————-+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
2 创建EC2 API端点 {% highlight sh %}
keystone endpoint-create –region regionOne –service-id $(keystone service-list | awk ‘/ ec2 / {print $2}’) \
--publicurl "http://$CONTROLLER_PUBLIC_ADDRESS:8773/services/Cloud" \
--adminurl "http://$CONTROLLER_ADMIN_ADDRESS:8773/services/Admin" \
--internalurl "http://$CONTROLLER_INTERNAL_ADDRESS:8773/services/Cloud"
+————-+——————————————–+
| Property | Value |
+————-+——————————————–+
| adminurl | http://controller:8773/services/Admin |
| id | b903c22bab8d412b96ff6839f5131f24 |
| internalurl | http://controller:8773/services/Cloud |
| publicurl | http://192.168.234.202:8773/services/Cloud |
| region | RegionOne |
| service_id | a18a1b887b484ed6a1130174ccb8eb5f |
+————-+——————————————–+
{% endhighlight %}
$EC2_SERVICE就是上一条命令创建的a18a1b887b484ed6a1130174ccb8eb5f
本文中$CONTROLLER_PUBLIC_ADDRESS为:192.168.234.202,$CONTROLLER_ADMIN_ADDRESS为:10.0.0.11
重启服务
{% highlight sh %}
service nova-cert restart
service nova-api restart
{% endhighlight %}
3 验证安装
首先要为用户生成AK(access key)和SK(secret key),我们来为demo这个用户来生成AK和SK.
{% highlight sh %} $ keystone tenant-list +———————————-+———+———+ | id | name | enabled | +———————————-+———+———+ | 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 | admin | True | | 6245a74d882e451c8d7663a46103b8b2 | demo | True | | 0357b13cb33941bda442094eda169625 | lxl | True | | ef36de18149b4c809c4b26b63b6dda37 | service | True | | 04015ed1fdb94efb80bab7916fbf1660 | zlq | True | +———————————-+———+———+
$ keystone user-list +———————————-+—————————–+———+—————————–+ | id | name | enabled | email | +———————————-+—————————–+———+—————————–+ | c2ba205513e448098f0e0daf80f2f649 | admin | True | admin@example.com | | d839485477e44aa8baabbefd19829392 | ceilometer | True | | | fd7b1e90d1144b669d20040b9c334d88 | cinder | True | | | 54a55d3f3c1f4797bb82d196e6c02ccd | demo | True | demo@example.com | | 924b65933a294f0bb5e26945689c2c38 | glance | True | | | 0c138994a2304fe5b38eb2a709d6e3fd | liqiang.zhang@ecloud.com.cn | True | liqiang.zhang@ecloud.com.cn | | f0d885f2c2e9498189b61ebb28475f35 | lxl | True | xiaoreqing@126.com | | d9ea6a6733934f139a42dfad12f1009a | neutron | True | | | 952eae64d8124b06812a5bb595f3690f | nova | True | | +———————————-+—————————–+———+—————————–+
$ keystone ec2-credentials-create –tenant-id=357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 –user-id=c2ba205513e448098f0e0daf80f2f649 +———–+———————————-+ | Property | Value | +———–+———————————-+ | access | 6ccf7c40bebe4984964e1ada23680941 | | secret | 6cdaaa769e3c4fb58aeac0de49b01658 | | tenant_id | 357abecb4def441eb7a36e7cf5d173c4 | | trust_id | | | user_id | c2ba205513e448098f0e0daf80f2f649 | +———–+———————————-+ {% endhighlight %}
把下面的变量加入admin-openrc.sh
{% highlight sh %} export EC2_ACCESS_KEY=6ccf7c40bebe4984964e1ada23680941 export EC2_SECRET_KEY=6cdaaa769e3c4fb58aeac0de49b01658 export EC2_URL=http://controller:8773/services/Cloud {% endhighlight %}
参考:
https://github.com/openstack/keystone/blob/master/tools/sample_data.sh
https://github.com/gc3-uzh-ch/gridka-school/blob/master/tutorial/nova_api.rst
